Bladder cancer

What is the urinary bladder?
The urinary bladder is a hollow, muscular organ that stores urine before it is expelled from the body.
It is part of the urinary tract and is located in the lower abdomen, just behind the pubic bone.
When full, the bladder sends signals to the brain, triggering the urge to urinate. The bladder then contracts, pushing urine through the urethra and out of the body. The bladder works together with a sphincter muscle, which wraps around the urethra and helps control the release of urine.
What is bladder cancer?
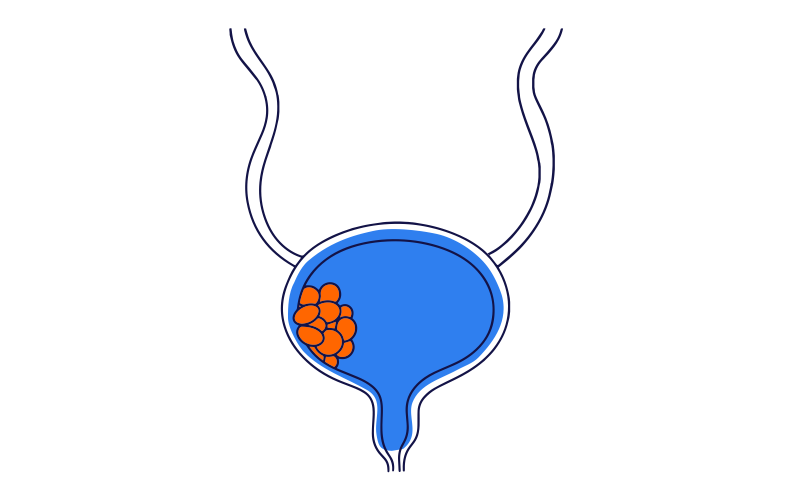
Bladder cancer is a disease caused by the abnormal growth of cells in the bladder.
It occurs when cells from the lining of the bladder grow uncontrollably, forming a tumour that can spread to other parts of the body.
Bladder cancer is more common in older adults. The main risk factors for developing bladder cancer are smoking and exposure to chemicals in the dye, rubber, paint, and petrochemical industries.
What are the symptoms of bladder cancer?
The most common symptom of bladder cancer is blood in the urine.
Sometimes bladder cancer can cause change in bladder habbits such as the need to urinate frequently or urgently, or pain when urinating.
Advanced bladder cancer can cause pain in the pelvis or back.

Blood in the urine

Frequent or urgent urination

Painful urination

Pelvic pain

Back pain
How is bladder cancer diagnosed?
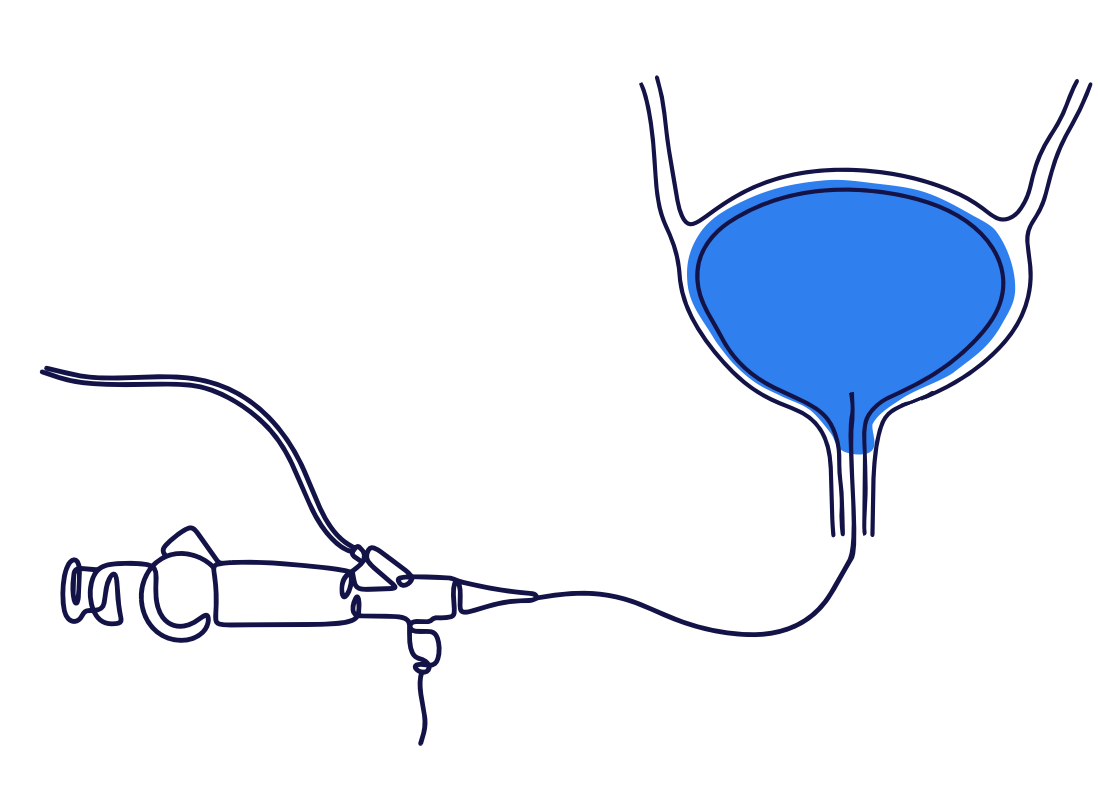
Bladder cancer is usually diagnosed by looking into the bladder with a camera, a procedure know as a cystoscopy.
If a cancer is found, a biopsy can be taken to be looked at under a microscope. This will determine the type of cancer and how aggressive it is.
Urine tests and scans are also used in the diagnosis of bladder cancer.
How is bladder cancer treated?
Early bladder cancer can be treated with minimally invasive surgery known as a Transurethral Resection of a Bladder Tumour (TURBT).
Sometimes chemotherapy or immunotherapy is given directly into the bladder to reduce the chance of bladder cancer coming back after a TURBT. This is known as intravesical therapy.
Advanced bladder cancer can be treated with a combination of surgery to remove the bladder, known as a cystectomy, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and immunotherapy.
Read more about the procedures we use to diagnose and treat bladder cancer below.
Meet our team
Meet our team of experienced Urologists who diagnose and treat bladder cancer.