Bladder pain sydrome (interstitial cystitis)
What is bladder pain syndrome?
Bladder pain syndrome (BPS), formerly known interstitial cystitis (IC), is a is a chronic condition affecting the bladder and pelvic organs.
BPS is characterised by persistent pain, discomfort or pressure in the bladder and pelvic region. The pain is often worse when the bladder is full.
This pain is usually accompanied by urinary symptoms, incuding the need to urinate urgently and frequently through the day and night.
The severity of symptoms can vary from mild to severe and can fluctuate over time.
The symptoms of BPS are commonly mistaken for a urinary tract infection.

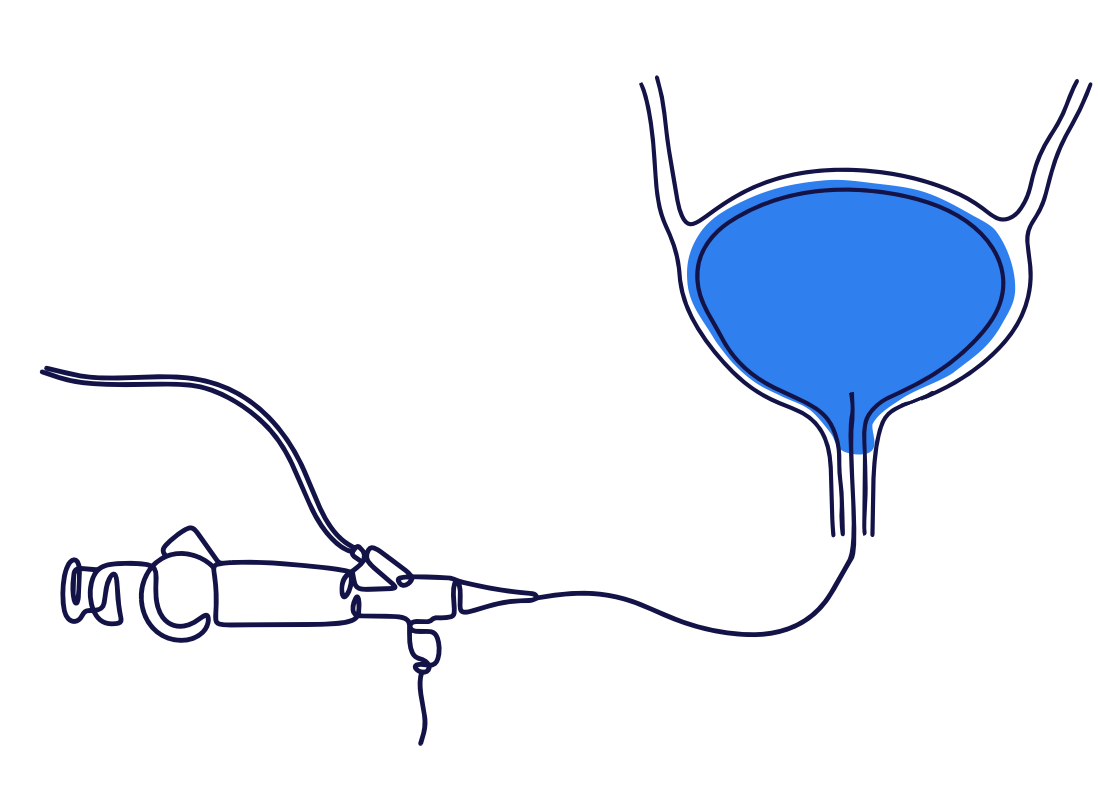
What is the urinary bladder?
The urinary bladder is a hollow, muscular organ that stores urine before it is expelled from the body.
It is part of the urinary tract and is located in the lower abdomen, just behind the pubic bone.
When full, the bladder sends signals to the brain, triggering the urge to urinate. The bladder then contracts, pushing urine through the urethra and out of the body. The bladder works together with a sphincter muscle, which wraps around the urethra and helps control the release of urine.
What causes bladder pain syndrome?
The exact cause of BPS is not known.
It’s thought that a combination of factors, including defects in the lining of the bladder, nerve sensitivity, overactivity of the pelvic muscles, and the immune system, may contribute to the symptoms.
Urinary tract infections are common in people with BPS, but it’s unknown exactly what role infection plays in the condition.
BPS is more common in women but can occur in men and can occur at any age. It is more common in people with other conditions that cause pelvic pain, including endometriosis and irritable bowel syndrome.
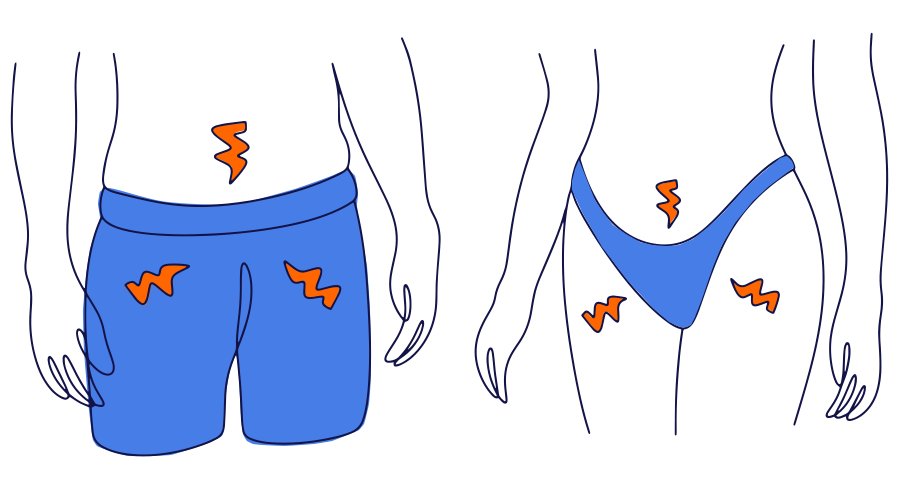
What are the symptoms of bladder pain syndrome?
BPS causes bladder/pelvic pain and urinary symptoms, including urinary frequency, urgency, and waking at night to pass urine.

Pelvic pain

Frequent or urgent urination

Nocturia
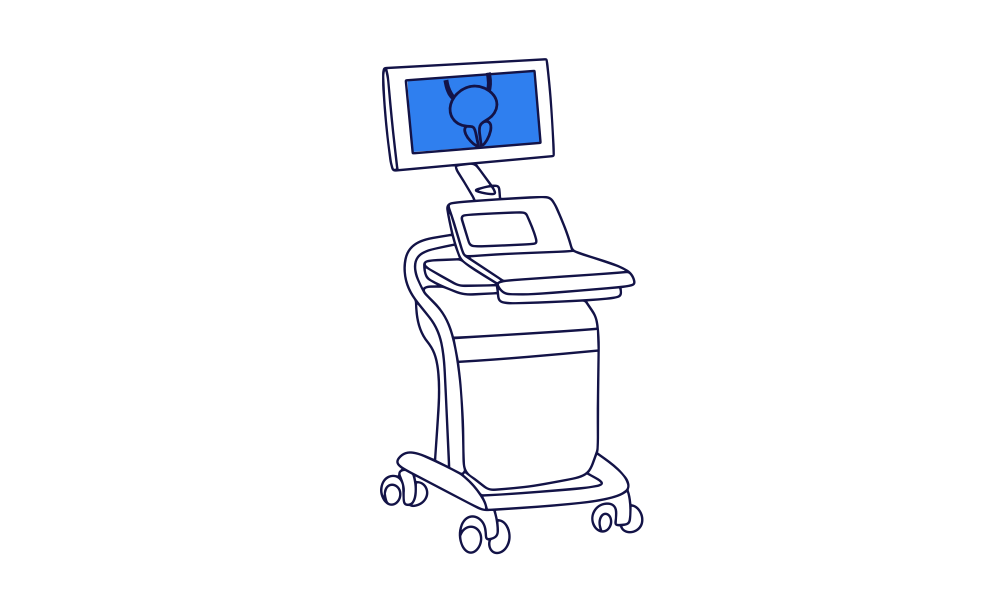
How is bladder pain syndrome diagnosed?
BPS can be diagnosed through a combination of symptoms and tests.
Initial tests may include a urine test and an ultrasound scan.
A cystoscopy can be used to help diagnose the condition, and exclude other causes for the symptoms.
How is bladder pain syndrome treated?
BPS often requires a combination of treatments to control the symptoms.
Treatment options include:
- Dietary modification to remove bladder irritants from the diet
- Physiotherapy
- Medications to treat inflammation and nerve pain and to restore the lining of the bladder
- Instillations and injections into the bladder
Rarely, for very severe and advanced cases of BPS, an operation to remove the bladder, known as a cystectomy, is required.