Prostate cancer
What is the prostate?
The prostate is a walnut-sized gland in men.
It is located just below the bladder, surrounding the urethra (the tube that carries urine and semen out of the body).
The prostate is part of the male reproductive system. Its function is to produce seminal fluid that nourishes and protects sperm. This fluid makes up the majority of semen.
What is prostate cancer?
Prostate cancer is a disease cause by abnormal growth of cells in the prostate.
These cells have the potential to grow within the prostate and to spread to other parts of the body.
Prostate cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer in Australia. It is more common in older men and in men who have a father or brother with prostate cancer.
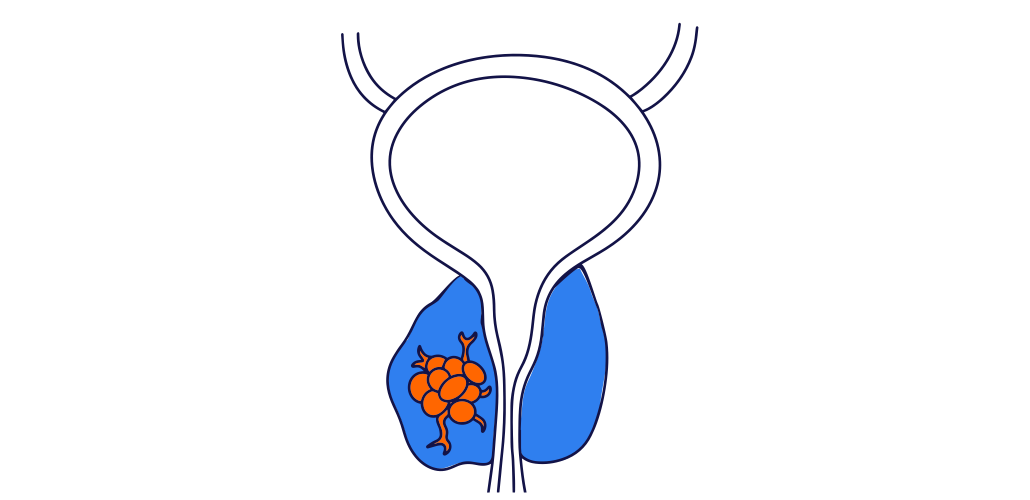
What are the symptoms of prostate cancer?
Most early prostate cancer has no symptoms.
Occassionally, advanced prostate cancer can cause bladder symptoms such as a change in bladder habits or blood in the urine or semen.
Prostate cancer which has spread beyond the prostate can cause back pain, bone pain or unexplained weight loss.

No symptoms

Change in bladder habbits

Blood in the urine

Blood in semen

Back pain
Bone pain

Unexplained weight loss
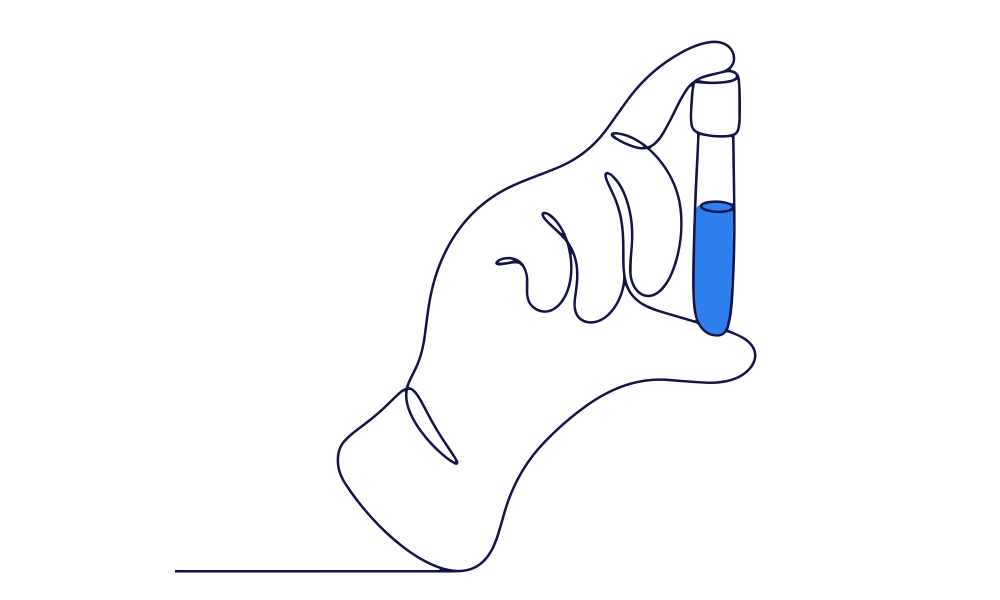
How is prostate cancer diagnosed?
Early prostate cancer usually has no symptoms. Most early prostate cancer is detected by a blood test called Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA).
If your PSA test is abnormaly high, further investigation may be required to diagnose or exclude prostate cancer. Investigations can include a prostate examination, an MRI scan, or a prostate biopsy.
How is prostate cancer treated?
Prostate cancer can often be safely managed with surveillance.
Aggressive prostate cancer which is confined to the prostate (localised) can be treated with surgery known as radical prostatectomy, radiation therapy, or focal therapy.
Prostate cancer which has spread to other parts of the body (advanced or metastatic) can be treated with hormone therapy, chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
Read more about the procedures we use to diagnose and treat prostate cancer below.
What are the side effects of prostate cancer treatment?
Many men who have treatment for prosate cancer will have an excellent recovery with few or no long term side effects.
Unfortunately, some men will experience long-term side effects of treatment, including problems with urinary, sexual or bowel function, and psychological distress.
Read more about the conditions which can be associated with prostate cancer treatment below.

Psychological support for prostate cancer patients
Our team also includes Prof Suzanne Chambers, Health Psychologist, who has a special interest in supporting men with prostate cancer, including stress and anxiety management, decision support, coaching in coping skills, managing relationships and planning for wellbeing.