Urinary Tract Infections
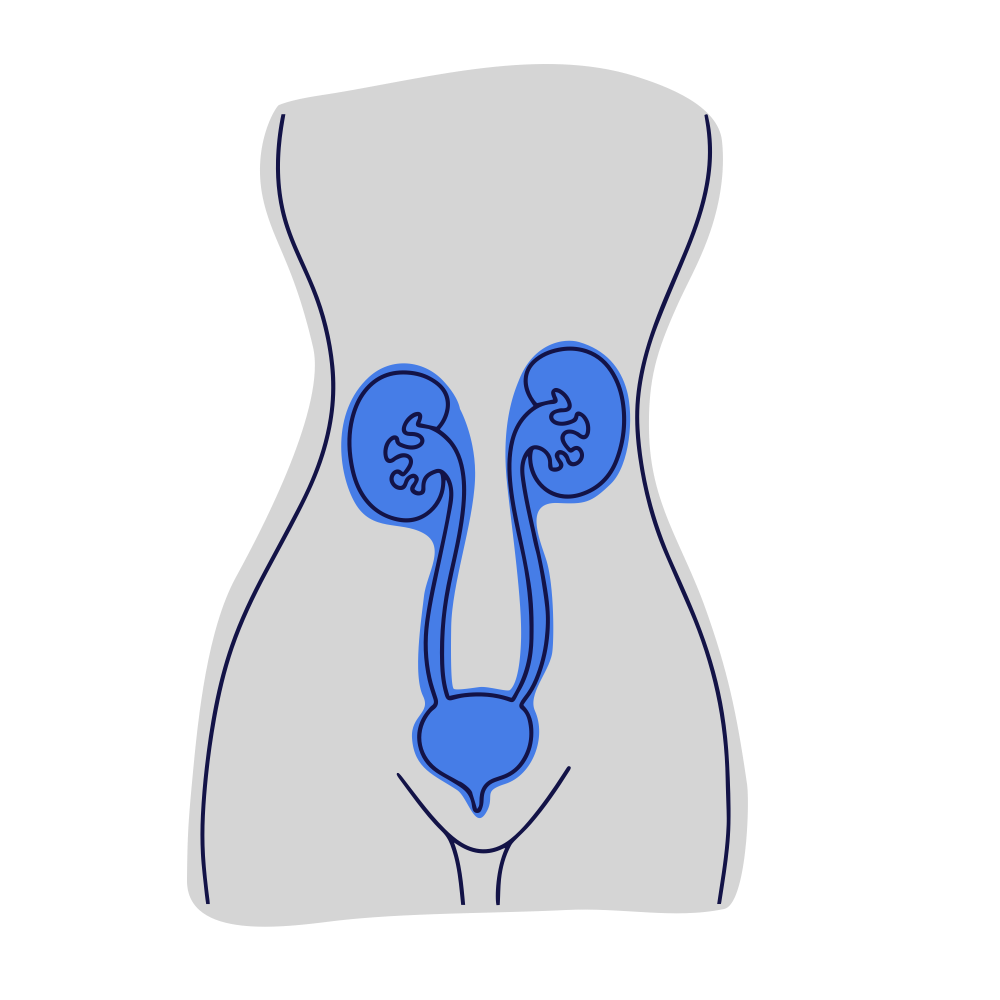
What is the urinary tract?
The urinary tract is the system in your body responsible for producing, storing, and eliminating urine.
The urinary tract includes:
The Kidneys – two bean-shaped organs which filter waste and excess fluids from your blood to produce urine.
The Ureters – two tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
The Bladder – a muscular sac that stores urine until it’s ready to be expelled.
The Urethra – the tube which you pass urine through.
The Prostate – a walnut sized gland which surrounds the urethra, found only in men.
What is a urinary tract infection?
A urinary tract infection (UTI), also known as cystitis, is a bacterial infection of the bladder.
Cystitis can spread to involve other organs in the urinary tract, including the kidneys (pyelonephritis), prostate (prostatitis), and testes (orchitis).
What are the symptoms of urinary tract infections?
Common symptoms of a UTI include the need to urinate frequently or urgently, and pain when passing urine.
Less common symptoms include blood in the urine, back pain, and fevers. These symptoms can indicate a more serious infection is developing.

Frequent or urgent urination

Painful urination

Blood in the urine

Back pain
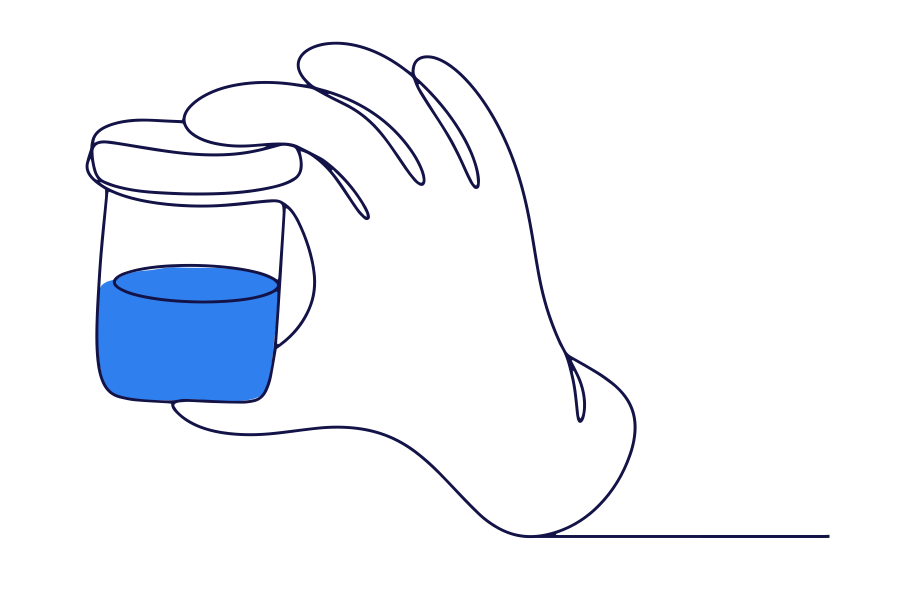

How is a urinary tract infection diagnosed?
Urinary tract infections are diagnosed by doing a test on a urine sample to look for inflammation and bacteria.
How are urinary tract infections managed?
Most urinary tract infections can be treated with a combination or oral antibiotics, increased water intake, and a urinary alkaliniser.
Recurrent UTI’s in women (3 or more per year) and any UTI in a man can be a sign of a problem with the urinary tract, and warrants further investigation.
Further investigation can include urine tests, ultrasound or CT scans of the urinary tract, a Cystoscopy, or Urodynamics studies.